在使用Spring的IoC的时候传统使用XML的<bean>标签进行配置;在实际项目开发中,需要配置的bean数量庞大,因此出现以下缺陷,一方面配置较为麻烦;另一方面使得配置文件的变得臃肿;因此Spring2.5开始引入了通过注解的方式来注入依赖关系等;要使用注解需要JDK1.5以上的JDK,因为底层才能够访问注解源码。
在使用Spring的IoC的时候传统使用XML的<bean>标签进行配置;在实际项目开发中,需要配置的bean数量庞大,因此出现以下缺陷,一方面配置较为麻烦;另一方面使得配置文件的变得臃肿;因此Spring2.5开始引入了通过注解的方式来注入依赖关系等;要使用注解需要JDK1.5以上的JDK,因为底层才能够访问注解源码。
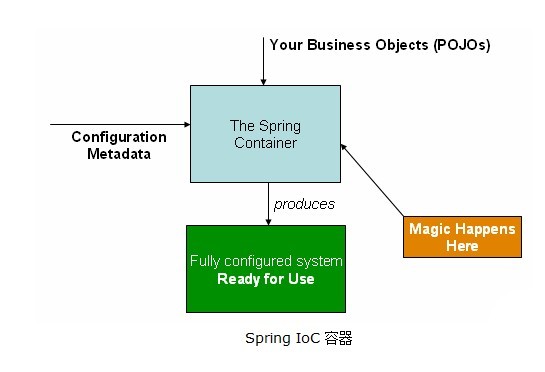
在使用Spring的注解前,需要在配置文件中开启注解功能,如下配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="https://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd">
<!--
Activates(激活) various(多种) annotations to be detected(检测) in bean classes:
Spring's @Required and @Autowired, as well as(以及) JSR 250's @PostConstruct,
@PreDestroy and @Resource (if available), JAX-WS's @WebServiceRef (if available),
EJB3's @EJB (if available), and JPA's @PersistenceContext and @PersistenceUnit
(if available). Alternatively(或者), you may choose to activate the individual(个别的)
BeanPostProcessors for those annotations.
Note: This tag does not activate processing of Spring's @Transactional or EJB3's
@TransactionAttribute annotation. Consider(考虑) the use of the <tx:annotation-driven>
tag for that purpose. -->
<context:annotation-config />
<!--
Scans(扫描) the classpath for annotated components that will be auto-registered as
Spring beans. By default, the Spring-provided @Component, @Repository,
@Service, and @Controller stereotypes will be detected.
Note: This tag implies(表明) the effects of the 'annotation-config' tag, activating
@Required,@Autowired, @PostConstruct, @PreDestroy, @Resource, @PersistenceContext
and @PersistenceUnit annotations in the component classes, which is usually(通常)
desired(希望) for autodetected components(without external configuration). Turn off
the 'annotation-config' attribute to deactivate this default behavior, for example
in order to use custom BeanPostProcessor definitions for handling those annotations.
Note: You may use placeholders(占位符) in package paths, but only resolved(解决)
against system properties (analogous(类似) to resource paths). A component scan
results in new bean definition being registered; Spring's PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
will apply to those bean definitions just like to regular bean definitions,
but it won't apply to the component scan settings themselves.
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="ioc.autowired"/>
</beans>
注意:
(1)需要引入xmlns:context="https://www.springframework.org/schema/context"命名空间以及对应的模式文件(xsd);
(2)<context:annotation-config /> 启用注解功能,同时还需要配置<context:component-scan base-package="ioc.autowired"/>去扫描指定基础包中所有类的注解,然后将注解表示的类注册到容器中;
spring广告位
使用@Repository注解将DAO层(即数据库层)作为Spring的bean,如下代码:
package ioc.autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* 用于测试的Dao层
* @author huangxin
* @date 2016年1月16日22:02:52
*/
@Repository
public class DemoDao {
public void show() {
System.out.println( this.getClass().getName() + " => show()");
}
}使用@Service("demoService")注解将服务层的类作为Spring的bean注册到容器中,如下:
package ioc.autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("demoService")
public class DemoService {
@Autowired
private DemoDao demoDao;
public void show() {
demoDao.show();
}
}客户端代码:
package ioc.autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String xmlPath = "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
DemoService demoService = context.getBean(DemoService.class);
demoService.show();
}
}上面就是一个简单的Spring入门级注解Demo。









