MongoDB 查询分析可以确保我们所建立的索引是否有效,是查询语句性能分析的重要工具。MongoDB 查询分析常用函数有 explain() 和 hint()。
数据准备
为了更好的理解 explain() 函数,这里采用脚本的方式创建 100万用户数据,脚本如下:
> var chas = ['A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I','K','L','M','N','O']
> for(var i=0; i < 1000000; i++){
... db.users.insertOne({ name: chas[Math.ceil(Math.random()*chas.length)] + "name", age:Math.ceil(Math.random()*100) })
... }
{
"acknowledged" : true,
"insertedId" : ObjectId("6503af99f470730f2bb44244")
}
上面脚本将在 mongo 客户端中执行,执行后的结果集内容如下:
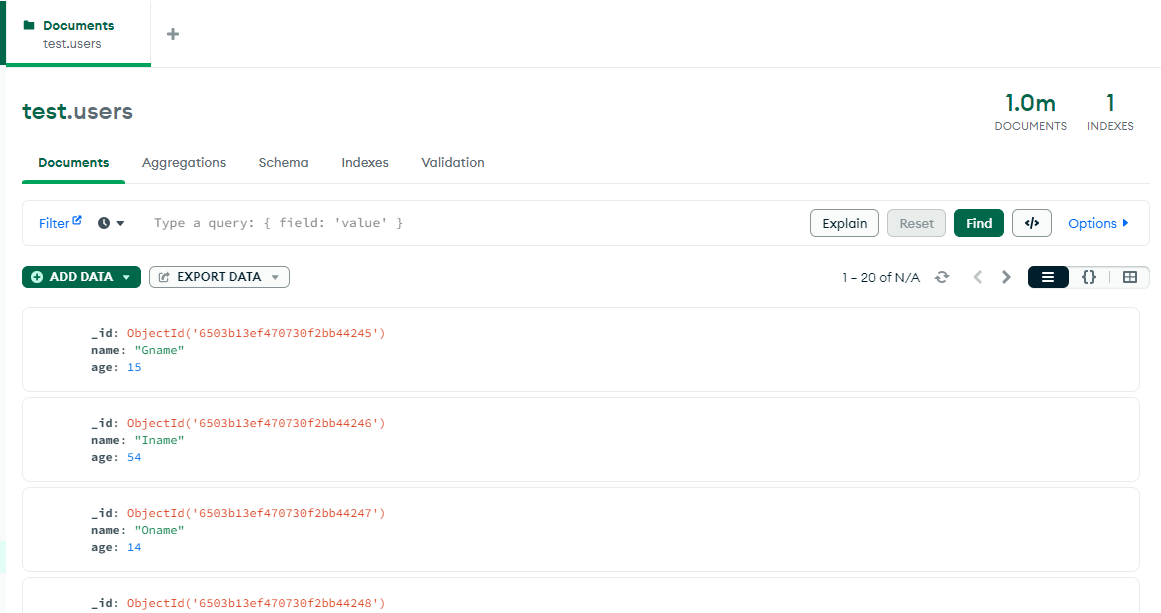
从上图可知,刚好 100 万用户数据,用户数据只包含了 name 和 age。
mongodb广告位
explain()
在 MongoDB 中,可以使用 explain() 方法来进行查询分析。explain() 方法可以返回查询的执行计划和相关统计信息,帮助我们了解查询的性能和优化情况。
explain() 方法使用的基本语法如下:
db.collection.find(query).explain()
其中,db.collection.find(query) 是要进行分析的查询语句。
explain() 方法返回的结果包含了以下重要的字段:
{
"explainVersion" : "1",
"queryPlanner" : {
// 查询规划器的信息,包括查询使用的索引、查询计划和查询优化器的相关信息
},
"command" : {
// 执行的命令
},
"serverInfo" : {
// MongoDB 服务器的信息,包括服务器版本、操作系统等
},
"serverParameters" : {
// 服务参数信息
},
"ok" : 1
}
如果运行如下命令:
db.users.find().explain()
完整的输出如下:
{
"explainVersion" : "1",
// 查询计划
"queryPlanner" : {
// 在哪里执行查询,在 test 数据库的 users 集合中执行查询
"namespace" : "test.users",
"indexFilterSet" : false,
// 查询参数解析
"parsedQuery" : {
},
"queryHash" : "8B3D4AB8",
"planCacheKey" : "D542626C",
"maxIndexedOrSolutionsReached" : false,
"maxIndexedAndSolutionsReached" : false,
"maxScansToExplodeReached" : false,
// 最终胜出的查询计划,如果有多个匹配的索引时,mongodb 会为每个匹配
"winningPlan" : {
// 扫描整个集合
"stage" : "COLLSCAN",
"direction" : "forward"
},
// 被拒绝的查询计划,即没有获胜的查询计划
"rejectedPlans" : [ ]
},
// 执行的命令,在 test 数据库的 users 集合中执行 find 命令,没有过滤条件
"command" : {
"find" : "users",
"filter" : {
},
"$db" : "test"
},
// 服务信息,如:主机地址、端口、mongodb 版本信息
"serverInfo" : {
"host" : "hxstrive",
"port" : 27017,
"version" : "5.0.20",
"gitVersion" : "2cd626d8148120319d7dca5824e760fe220cb0de"
},
// 服务参数信息
"serverParameters" : {
"internalQueryFacetBufferSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryFacetMaxOutputDocSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalLookupStageIntermediateDocumentMaxSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalDocumentSourceGroupMaxMemoryBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryMaxBlockingSortMemoryUsageBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryProhibitBlockingMergeOnMongoS" : 0,
"internalQueryMaxAddToSetBytes" : 104857600,
"internalDocumentSourceSetWindowFieldsMaxMemoryBytes" : 104857600
},
"ok" : 1
}
explain() 示例一
(1)在 users 集合的 name 和 age 字段上面创建索引:
> db.users.createIndex({ name:1, age:-1 })
{
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"ok" : 1
}
> db.users.createIndex({ age:-1, name:1 })
{
"numIndexesBefore" : 2,
"numIndexesAfter" : 3,
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"ok" : 1
}
(2)在查询语句中使用 explain 查看查询计划:
> db.users.find({ age:45, name:/D.+/ }).explain()
{
"explainVersion" : "1",
"queryPlanner" : {
// 查询 test 数据库 users 集合
"namespace" : "test.users",
"indexFilterSet" : false,
// 查询条件,查询 age 和 name 字段
"parsedQuery" : {
"$and" : [
{
"age" : {
"$eq" : 45
}
},
{
"name" : {
"$regex" : "D.+"
}
}
]
},
"queryHash" : "4FA0B9FF",
"planCacheKey" : "65BB8DE0",
"maxIndexedOrSolutionsReached" : false,
"maxIndexedAndSolutionsReached" : false,
"maxScansToExplodeReached" : false,
// 获胜的查询计划
"winningPlan" : {
"stage" : "FETCH",
// 该阶段的输出将传递给父阶段 FETCH,作为 FETCH 阶段的输入
"inputStage" : {
// 使用索引
"stage" : "IXSCAN",
"filter" : {
"name" : {
"$regex" : "D.+"
}
},
"keyPattern" : {
"age" : -1,
"name" : 1
},
// 使用名为 age_-1_name_1 的索引
"indexName" : "age_-1_name_1",
"isMultiKey" : false,
"multiKeyPaths" : {
"age" : [ ],
"name" : [ ]
},
"isUnique" : false,
"isSparse" : false,
"isPartial" : false,
"indexVersion" : 2,
"direction" : "forward",
"indexBounds" : {
"age" : [
"[45.0, 45.0]"
],
"name" : [
"["", {})",
"[/D.+/, /D.+/]"
]
}
}
},
// 被拒绝的查询计划
"rejectedPlans" : [
{
"stage" : "FETCH",
"inputStage" : {
"stage" : "IXSCAN",
"filter" : {
"name" : {
"$regex" : "D.+"
}
},
"keyPattern" : {
"name" : 1,
"age" : -1
},
"indexName" : "name_1_age_-1",
"isMultiKey" : false,
"multiKeyPaths" : {
"name" : [ ],
"age" : [ ]
},
"isUnique" : false,
"isSparse" : false,
"isPartial" : false,
"indexVersion" : 2,
"direction" : "forward",
"indexBounds" : {
"name" : [
"["", {})",
"[/D.+/, /D.+/]"
],
"age" : [
"[45.0, 45.0]"
]
}
}
}
]
},
// 查询命令
"command" : {
"find" : "users",
"filter" : {
"age" : 45,
"name" : /D.+/
},
"$db" : "test"
},
// 服务器信息
"serverInfo" : {
"host" : "hxstrive",
"port" : 27017,
"version" : "5.0.20",
"gitVersion" : "2cd626d8148120319d7dca5824e760fe220cb0de"
},
// 服务器参数信息
"serverParameters" : {
"internalQueryFacetBufferSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryFacetMaxOutputDocSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalLookupStageIntermediateDocumentMaxSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalDocumentSourceGroupMaxMemoryBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryMaxBlockingSortMemoryUsageBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryProhibitBlockingMergeOnMongoS" : 0,
"internalQueryMaxAddToSetBytes" : 104857600,
"internalDocumentSourceSetWindowFieldsMaxMemoryBytes" : 104857600
},
"ok" : 1
}
plain 结果将查询计划以阶段树的形式呈现,每个阶段将其结果(文档或索引键)传递给父节点,叶节点访问集合或索引。中间节点操纵由子节点产生的文档或索引键。根节点是MongoDB 从中派生结果集的最后阶段。
MongoDB 常见的阶段描述如下:
COLLSCAN 集合扫描
IXSCAN 索引扫描
FETCH 检出文档
SHARD_MERGE 合并分片中结果
SHARDING_FILTER 分片中过滤掉孤立文档
LIMIT 使用limit 限制返回数
PROJECTION 使用 skip 进行跳过
IDHACK 针对_id进行查询
COUNT 利用db.coll.explain().count()之类进行count运算
COUNTSCAN count不使用Index进行count时的stage返回
COUNT_SCAN count使用了Index进行count时的stage返回
SUBPLA 未使用到索引的$or查询的stage返回
TEXT 使用全文索引进行查询时候的stage返回
PROJECTION 限定返回字段时候stage的返回
...
explain() 示例二
使用 explain("executionStats") 命令获取查询的执行统计信息,例如:
> db.users.find({ age:45, name:/D.+/ }).explain("executionStats")
{
"explainVersion" : "1",
// 查询计划
"queryPlanner" : {
"namespace" : "test.users",
"indexFilterSet" : false,
// 查询条件
"parsedQuery" : {
"$and" : [
{
"age" : {
"$eq" : 45
}
},
{
"name" : {
"$regex" : "D.+"
}
}
]
},
"maxIndexedOrSolutionsReached" : false,
"maxIndexedAndSolutionsReached" : false,
"maxScansToExplodeReached" : false,
// 胜出的查询计划
"winningPlan" : {
// 根据索引返回的 ObjectId 查询具体文档
"stage" : "FETCH",
"inputStage" : {
// 使用索引
"stage" : "IXSCAN",
"filter" : {
"name" : {
"$regex" : "D.+"
}
},
"keyPattern" : {
"age" : -1,
"name" : 1
},
// 使用名为 age_-1_name_1 的索引
"indexName" : "age_-1_name_1",
"isMultiKey" : false,
"multiKeyPaths" : {
"age" : [ ],
"name" : [ ]
},
"isUnique" : false,
"isSparse" : false,
"isPartial" : false,
"indexVersion" : 2,
"direction" : "forward",
"indexBounds" : {
"age" : [
"[45.0, 45.0]"
],
"name" : [
"["", {})",
"[/D.+/, /D.+/]"
]
}
}
},
// 被拒绝的查询计划
"rejectedPlans" : [
{
"stage" : "FETCH",
"inputStage" : {
"stage" : "IXSCAN",
"filter" : {
"name" : {
"$regex" : "D.+"
}
},
"keyPattern" : {
"name" : 1,
"age" : -1
},
"indexName" : "name_1_age_-1",
"isMultiKey" : false,
"multiKeyPaths" : {
"name" : [ ],
"age" : [ ]
},
"isUnique" : false,
"isSparse" : false,
"isPartial" : false,
"indexVersion" : 2,
"direction" : "forward",
"indexBounds" : {
"name" : [
"["", {})",
"[/D.+/, /D.+/]"
],
"age" : [
"[45.0, 45.0]"
]
}
}
}
]
},
// 执行状态
"executionStats" : {
"executionSuccess" : true,
// 本次查询返回的文档数量。
"nReturned" : 710,
// 数据库执行本次查询所花费的毫秒数。这个数字越小越好。
"executionTimeMillis" : 34,
// 如果使用了索引,那么这个数字就是查找过的索引条目数量。
// 如果本次查询是一次全表扫描,那么这个数字就表示检查过的文档数量。
"totalKeysExamined" : 10168,
// MongoDB 按照索引指针在磁盘上查找实际文档的次数。
// 如果查询中包含的查询条件不是索引的一部分,或者请求的字段没有包含在索引中,MongoDB 就必须查找每个索引项所指向的文档。
"totalDocsExamined" : 710,
"executionStages" : {
"stage" : "FETCH",
"nReturned" : 710,
"executionTimeMillisEstimate" : 9,
"works" : 10168,
"advanced" : 710,
"needTime" : 9457,
// 为了让写请求顺利进行,本次查询所让步(暂停)的次数。如果有写操作在等待执行,那么查询将定期释放它们的锁以允许写操作执行。
// 在本次查询中,由于并没有写操作在等待,因此查询永远不会进行让步。
"needYield" : 0,
"saveState" : 11,
"restoreState" : 11,
"isEOF" : 1,
"docsExamined" : 710,
"alreadyHasObj" : 0,
"inputStage" : {
// MongoDB 是否可以使用索引完成本次查询。如果不可以,那么会使用 "COLLSCAN" 表示必须执行集合扫描来完成查询。
// IXSCAN 表示使用了索引
"stage" : "IXSCAN",
"filter" : {
"name" : {
"$regex" : "D.+"
}
},
// 返回的键数
"nReturned" : 710,
// 索引执行时间
"executionTimeMillisEstimate" : 3,
"works" : 10168,
"advanced" : 710,
"needTime" : 9457,
"needYield" : 0,
"saveState" : 11,
"restoreState" : 11,
"isEOF" : 1,
"keyPattern" : {
"age" : -1,
"name" : 1
},
// 索引名称
"indexName" : "age_-1_name_1",
"isMultiKey" : false,
"multiKeyPaths" : {
"age" : [ ],
"name" : [ ]
},
"isUnique" : false,
"isSparse" : false,
"isPartial" : false,
"indexVersion" : 2,
"direction" : "forward",
"indexBounds" : {
"age" : [
"[45.0, 45.0]"
],
"name" : [
"["", {})",
"[/D.+/, /D.+/]"
]
},
"keysExamined" : 10168,
"seeks" : 1,
"dupsTested" : 0,
"dupsDropped" : 0
}
}
},
"command" : {
"find" : "users",
"filter" : {
"age" : 45,
"name" : /D.+/
},
"$db" : "test"
},
"serverInfo" : {
"host" : "hxstrive",
"port" : 27017,
"version" : "5.0.20",
"gitVersion" : "2cd626d8148120319d7dca5824e760fe220cb0de"
},
"serverParameters" : {
"internalQueryFacetBufferSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryFacetMaxOutputDocSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalLookupStageIntermediateDocumentMaxSizeBytes" : 104857600,
"internalDocumentSourceGroupMaxMemoryBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryMaxBlockingSortMemoryUsageBytes" : 104857600,
"internalQueryProhibitBlockingMergeOnMongoS" : 0,
"internalQueryMaxAddToSetBytes" : 104857600,
"internalDocumentSourceSetWindowFieldsMaxMemoryBytes" : 104857600
},
"ok" : 1
}
mongodb广告位
hint()
在 MongoDB 中,可以使用 hint() 方法来指定查询使用的索引。hint() 方法用于强制查询使用指定的索引,以便优化查询性能。
hint() 方法的基本语法如下:
db.collection.find(query).hint(index)
其中,db.collection.find(query) 是要进行查询的语句,index 是要使用的索引的名称或索引键。
hint() 示例
假设我们有一个名为 col 的集合,其中包含了用户信息,我们可以使用 hint() 方法来指定查询使用的索引。例如:
# 通过索引名
> db.col.find({ age:{ $gt:25 } }).hint("age_-1")
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a134"), "name" : "何八", "age" : 42, "email" : "heba@outlook.com", "sex" : "male" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a133"), "name" : "顾七", "age" : 30, "email" : "guqi@qq.com guq@163.com", "sex" : "male" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a131"), "name" : "王五", "age" : 27, "email" : "wangwu@sina.com.cn", "sex" : "male" }
# 通过指定字段方式使用索引
> db.col.find({ age:{ $gt:25 } }).hint({ age:-1 })
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a134"), "name" : "何八", "age" : 42, "email" : "heba@outlook.com", "sex" : "male" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a133"), "name" : "顾七", "age" : 30, "email" : "guqi@qq.com guq@163.com", "sex" : "male" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a131"), "name" : "王五", "age" : 27, "email" : "wangwu@sina.com.cn", "sex" : "male" }
上述示例中,我们使用 hint() 方法指定查询使用 age 字段的索引。这样可以确保查询使用该索引进行优化,提高查询性能。
如果指定了一个不存在的索引,则查询操作会报错:
> db.col.find({ age:{ $gt:25 } }).hint({ age:1 })
Error: error: {
"ok" : 0,
"errmsg" : "error processing query: ns=test.colTree: age $gt 25.0
Sort: {}
Proj: {}
planner returned error :: caused by :: hint provided does not correspond to an existing index",
"code" : 2,
"codeName" : "BadValue"
}
这是因为 col 集合中没有 age 字段为升序的索引(age_1),只有 age 降序索引(age_-1),如下:
> db.col.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"name" : 1
},
"name" : "name_1"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"age" : -1
},
"name" : "age_-1"
}
]
如果索引是一个多字段索引,hint() 该如何指定呢?
> db.col.getIndexes()
[
...
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"age" : -1,
"name" : 1
},
"name" : "age_-1_name_1"
}
]
# 方式一
> db.col.find({ age:{ $gt:25 } }).hint("age_-1_name_1")
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a134"), "name" : "何八", "age" : 42, "email" : "heba@outlook.com", "sex" : "male" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a133"), "name" : "顾七", "age" : 30, "email" : "guqi@qq.com guq@163.com", "sex" : "male" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a131"), "name" : "王五", "age" : 27, "email" : "wangwu@sina.com.cn", "sex" : "male" }
# 方式二
> db.col.find({ age:{ $gt:25 } }).hint({ age:-1, name:1 })
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a134"), "name" : "何八", "age" : 42, "email" : "heba@outlook.com", "sex" : "male" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a133"), "name" : "顾七", "age" : 30, "email" : "guqi@qq.com guq@163.com", "sex" : "male" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("64e71af810366fa87109a131"), "name" : "王五", "age" : 27, "email" : "wangwu@sina.com.cn", "sex" : "male" }
注意:
(1)使用 hint() 方法指定索引并不一定会提高查询性能。在大多数情况下,MongoDB 会自动选择合适的索引来执行查询。只有在特定情况下,当我们了解查询模式并且确定使用指定索引可以优化查询性能时,才应该使用 hint() 方法来指定索引。
(2)hint() 方法只对当前查询有效,不会影响其他查询。并且,使用 hint() 方法时需要确保指定的索引存在于集合中。


