前面章节介绍了 Eureka 客户端和服务端的启动过程,同时也分析了 EnableDiscoveryClient 类的源码,本章节将介绍 Eureka 服务端是怎样实现服务注册的。
我们通过在 AbstractInstanceRegistry 类中的 void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) 方法打断点,查看调用该方法的栈,如下图:
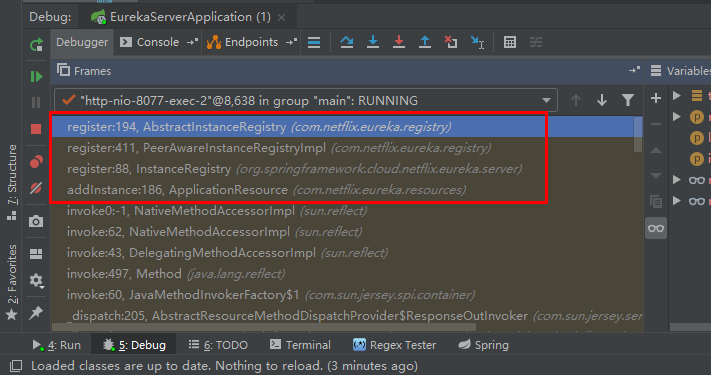
我们将依次分析上图中的 ApplicationResource、InstanceRegistry、PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl 和 AbstractInstanceRegistry 类关于服务注册部分逻辑。
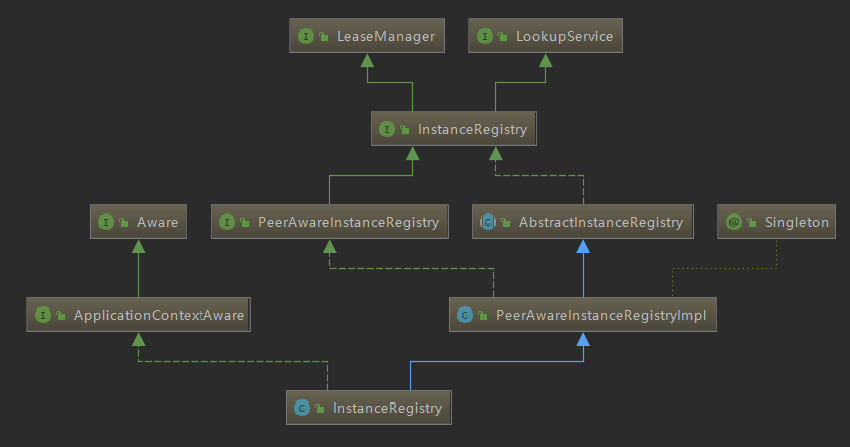
InstanceRegistry 类继承层次图如下:
spring cloud 广告位
ApplicationResource
该类将提供一个 POST 类型的 HTTP 接口供 Eureka 客户端调用,通过该接口可以将 Eureka 客户端的基础信息注册到 Eureka 服务端。该方法实现源码如下:
/**
* Registers information about a particular instance for an
* {@link com.netflix.discovery.shared.Application}.
*
* @param info
* {@link InstanceInfo} information of the instance. 实例信息
* @param isReplication
* a header parameter containing information whether this is
* replicated from other nodes. 一个 HTTP 头参数,指定是否从其他节点复制服务信息
*/
@POST
@Consumes({"application/json", "application/xml"})
public Response addInstance(InstanceInfo info,
@HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication) {
logger.debug("Registering instance {} (replication={})", info.getId(), isReplication);
// validate that the instanceinfo contains all the necessary required fields
// 验证 instanceinfo 是否包含所有必需的必需字段
//...
// handle cases where clients may be registering with bad DataCenterInfo with missing data
// 处理客户端可能向缺少数据的错误 DataCenterInfo 注册的情况
DataCenterInfo dataCenterInfo = info.getDataCenterInfo();
if (dataCenterInfo instanceof UniqueIdentifier) {
String dataCenterInfoId = ((UniqueIdentifier) dataCenterInfo).getId();
//...
}
// 将注册业务交给 register() 方法处理
registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication));
return Response.status(204).build(); // 204 to be backwards compatible
}
InstanceRegistry
该类实现了 InstanceRegistry 接口。InstanceRegistry 接口继承了 LookupService 、LeaseManager 接口,提供应用实例的注册与发现服务。另外,它结合实际业务场景,定义了更加丰富的接口方法。这里仅仅分析 register() 方法,源码如下:
@Override
public void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {
// 触发一个 EurekaInstanceRegisteredEvent 事件,我们可以通过 ApplicationListener 监听该事件
handleRegistration(info, resolveInstanceLeaseDuration(info), isReplication);
// 调用父类的 register() 方法
// 父类为 PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl,继续分析 PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl 的 register()
super.register(info, isReplication);
}
private void handleRegistration(InstanceInfo info, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {
log("register " + info.getAppName() + ", vip " + info.getVIPAddress() + ", leaseDuration " + leaseDuration
+ ", isReplication " + isReplication);
publishEvent(new EurekaInstanceRegisteredEvent(this, info, leaseDuration, isReplication));
}
你可以通过 ApplicationListener 去监听 EurekaInstanceRegisteredEvent 事件,例如:
@Component
public class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if(event instanceof EurekaInstanceRegisteredEvent) {
System.out.println("服务注册Event");
}
}
}
PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl
InstanceRegistry 类在服务注册、续约、下线等操作完成后,会调用 PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl 的相关逻辑。而 PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl 中主要是添加了一个广播的功能,拥有了将服务实例的注册、续约、下线等操作同步到其它 Eureka Server 的能力。我们这里分析一下 register() 方法,源码如下:
/**
* Registers the information about the {@link InstanceInfo} and replicates
* this information to all peer eureka nodes. If this is replication event
* from other replica nodes then it is not replicated.
*
* @param info
* the {@link InstanceInfo} to be registered and replicated.
* @param isReplication
* true if this is a replication event from other replica nodes,
* false otherwise.
*/
@Override
public void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {
int leaseDuration = Lease.DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS;
if (info.getLeaseInfo() != null && info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs() > 0) {
leaseDuration = info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs();
}
// 调用父类 AbstractInstanceRegistry 注册服务
super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication);
// 广播消息,同步注册消息到其他节点
replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication);
}
将所有 Eureka 操作复制到其他 Eureka 节点(不包含当前 Eureka 节点),replicateToPeers() 方法源码如下:
/**
* Replicates all eureka actions to peer eureka nodes except for replication
* traffic to this node.
*/
private void replicateToPeers(Action action, String appName, String id,
InstanceInfo info /* optional */,
InstanceStatus newStatus /* optional */, boolean isReplication) {
Stopwatch tracer = action.getTimer().start();
try {
if (isReplication) {
numberOfReplicationsLastMin.increment();
}
// If it is a replication already, do not replicate again as this will create a poison replication
if (peerEurekaNodes == Collections.EMPTY_LIST || isReplication) {
return;
}
for (final PeerEurekaNode node : peerEurekaNodes.getPeerEurekaNodes()) {
// If the url represents this host, do not replicate to yourself.
// 排除当前主机
if (peerEurekaNodes.isThisMyUrl(node.getServiceUrl())) {
continue;
}
// 复制信息到对于的节点
replicateInstanceActionsToPeers(action, appName, id, info, newStatus, node);
}
} finally {
tracer.stop();
}
}
AbstractInstanceRegistry
该类用于处理来自 Eureka 客户端的所有注册表请求。register() 方法源码如下:
/**
* Registers a new instance with a given duration.
*
* @see com.netflix.eureka.lease.LeaseManager#register(java.lang.Object, int, boolean)
*/
public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {
// private final ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
// private final Lock read = readWriteLock.readLock();
// 只读锁
read.lock();
try {
// 所有的服务信息都添加到 registry 这个 map 中,
// 格式为:ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>>()
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName());
REGISTER.increment(isReplication);
// 如果没有该服务的信息,则新建,并添加到registry中
if (gMap == null) {
final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>();
gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap);
if (gMap == null) {
gMap = gNewMap;
}
}
// existingLease 信息即服务的一些注册时间等信息,主要是为了校验该服务是否过期,如果已过期,则剔除
Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId());
// Retain the last dirty timestamp without overwriting it, if there is already a lease
if (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) {
Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp();
Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp();
logger.debug("Existing lease found (existing={}, provided={}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);
// this is a > instead of a >= because if the timestamps are equal, we still take the remote transmitted
// InstanceInfo instead of the server local copy.
if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) {
logger.warn("There is an existing lease and the existing lease's dirty timestamp {} is greater" +
" than the one that is being registered {}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);
logger.warn("Using the existing instanceInfo instead of the new instanceInfo as the registrant");
registrant = existingLease.getHolder();
}
} else {
// The lease does not exist and hence it is a new registration
synchronized (lock) {
if (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews > 0) {
// Since the client wants to register it, increase the number of clients sending renews
this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews + 1;
updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();
}
}
logger.debug("No previous lease information found; it is new registration");
}
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration);
if (existingLease != null) {
lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp());
}
gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease);
recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(
System.currentTimeMillis(),
registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")"));
// This is where the initial state transfer of overridden status happens
if (!InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) {
logger.debug("Found overridden status {} for instance {}. Checking to see if needs to be add to the "
+ "overrides", registrant.getOverriddenStatus(), registrant.getId());
if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) {
logger.info("Not found overridden id {} and hence adding it", registrant.getId());
overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus());
}
}
InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId());
if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) {
logger.info("Storing overridden status {} from map", overriddenStatusFromMap);
registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap);
}
// Set the status based on the overridden status rules
InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication);
registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus);
// If the lease is registered with UP status, set lease service up timestamp
if (InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) {
lease.serviceUp();
}
registrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED);
recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease));
registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();
invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress());
logger.info("Registered instance {}/{} with status {} (replication={})",
registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getId(), registrant.getStatus(), isReplication);
} finally {
read.unlock();
}
}
服务注册信息最终存放到ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease>>,外层 map 的 key 即为应用的服务名,内层 map 的 key 为我们设置的eureka.instance.instance-id,设置成这种格式,当多个应用提供相同服务时,那么外层 map 的 key 都相同,内层 map 的 key 不同。



